Warehouse ventilation is an extremely important topic in today’s world. You take your health and...
OSHA Warehouse Temperature Regulations
As a warehouse worker, it is important to be aware of the temperatures surrounding your environment for your safety. High ambient temperatures can cause fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and an increased risk of heat-related illness, while low temperatures can make it difficult to work with your hands.
Each of these issues can ultimately affect your overall safety and well-being on the job, which is why it’s important to pay attention to the temperature within your workplace. Additionally, maintaining consistent temperatures can help prevent damage to products and equipment stored in the warehouse.
Planning for Warehouse Temperature Control

Working in a warehouse can be tough, but at MacroAir, we're committed to helping improve the comfort and safety of your employees. As the inventor of the High Volume, Low Speed (HVLS) industrial ceiling fan, we know a thing or two about warehouse safety.
Our technology is based on the principle that moving air slowly is more efficient, and our fans move air in all directions to keep things fresh and comfortable. Not only do our fans help regulate temperature and improve air quality, but they can also make you feel up to 15° F cooler just by adding one to your warehouse.
At MacroAir, we're constantly striving to push the boundaries and improve your quality of life through innovative engineering and product development. If you want to make your warehouse a more comfortable place to work, consider investing in a MacroAir fan.
Table of Contents
1. Does OSHA Set Warehouse Temperature Regulations?
2. OSHA's Recommended Warehouse Temperature Range
4. What Temperature is Too Hot or Cold?
5. What To Do If Temperatures are Extreme In Your Warehouse
6. Benefits of Adding MacroAir Fans
Does OSHA Set Warehouse Temperature Regulations?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) does not have specific warehouse temperature regulations However, the agency does require employers to provide a workplace free from recognized hazards that are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to employees. This includes ensuring temperatures in the workplace are not too hot or too cold by providing a recommended temperature to ensure employee safety
OSHA’s Recommended Warehouse Temperature Range
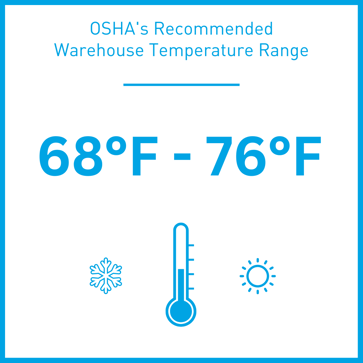
OSHA recommends that employers maintain a temperature range of 68-76° F in industrial environments, such as warehouses. If the warehouse temperature falls above or below the recommended range, employers must take the necessary steps to make their work environment more comfortable for their employees.
Why It Matters
Following OSHA’s temperature recommendations for industrial environments is important to maintain the safety and well-being of working individuals, improve productivity and efficiency, and protect the overall integrity of warehouse equipment and inventory.
Health and Well-Being of Workers
First and foremost, maintaining safe and comfortable warehouse temperatures helps protect the health and well-being of employees. Extreme temperatures can be dangerous and can lead to heat stroke or hypothermia if not properly managed. Additionally, workers can experience dehydration, fatigue, and increased slips, trips, and falls.
Although there aren’t set OSHA warehouse temperature regulations, by following the agency’s recommendations and promptly addressing any temperature-related concerns, employers and warehouse managers can help prevent issues from arising and ensure their employees can work safely and effectively.
Improve Productivity and Efficiency
In addition to protecting workers' health and well-being, maintaining the recommended temperature range can also help improve workplace efficiency and productivity. When workers experience temperatures that are too hot or cold, they may struggle to focus on tasks, leading to mistakes and slowdowns. By keeping the temperature at a comfortable level, warehouse managers can help ensure employees are working at their best.
Protect the Integrity of the Warehouse Equipment and Inventory
Finally, following OSHA's temperature recommendations can help protect the warehouse itself. Extreme temperatures can lead to equipment failure, which can disrupt facility operations and lead to costly repairs. By maintaining a safe and comfortable temperature, warehouse managers can help prevent equipment failure, maintain inventory integrity, and ensure the warehouse runs smoothly.
What Temperature is Too Hot or Cold?
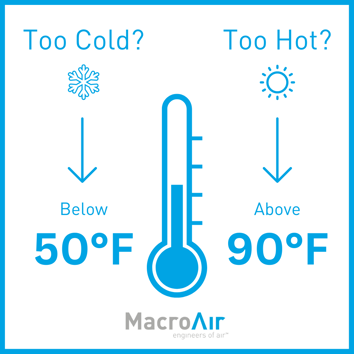
According to OSHA, the optimal temperature range for warehouses is between 68-76°F. At these temperatures, workers should be comfortable enough to focus on their tasks without feeling too hot or cold.
Temperatures above 90°F or below 50°F can be dangerous for warehouse workers. As previously mentioned, workers may be at risk of heat stroke or hypothermia. In hot environments, employees should take frequent breaks to rest and hydrate. In cold conditions, employees should dress in layers and use heating sources.
Employers may also need to provide fans to help cool the air in hot weather or warm the air in cold weather. Ultimately, the goal is to maintain a comfortable temperature for employees, allowing them to work safely and efficiently.
It's important to note that different people have different tolerance levels when it comes to temperature extremes, so it's essential for employers to listen to their employees and address any concerns they may have about the workplace environment. If you are a warehouse worker, you may need to speak up and bring your concerns to your boss or supervisor.
What to do if temperatures are extreme in your warehouse?

Be Aware of Available Resources
Title 8, California Code of Regulations (CCR), Section 3395 is a state regulation that sets guidelines for employers to follow to protect their employees from excessive heat in the workplace. The regulation applies to indoor and outdoor workplaces where the temperature is likely to exceed 80°F.
Under T8CCR 3395, employers are required to provide their employees with access to shade or air-conditioned areas, as well as cool drinking water. They must also develop a heat illness prevention plan that includes training for employees to recognize the symptoms of heat illness and how to prevent it.
Warehouse workers need to be aware of T8CCR 3395 and their employer's heat illness prevention plan to protect themselves from the dangers of excessive heat in the workplace. Heat illness can range from mild symptoms, such as heat cramps and heat exhaustion, to more serious conditions like heat stroke, which can be deadly.
Other states have similar regulations to protect workers from excessive heat in the workplace. For example, OSHA has guidelines for employers to follow to prevent heat illness in the workplace. It is important for workers to be aware of these regulations and to speak up if their employers are not monitoring their employees’ health and safety in the workplace.
OSHA’s Guidelines for Prevention of Heat-Related Illness
Some of the guidelines that OSHA recommends for employers to follow to prevent heat illness in the workplace include:
-
- Providing employees with water, rest, and shade to help prevent heat illness.
- Training employees on the symptoms of heat illness and how to prevent it.
- Monitoring employees for signs of heat illness and taking action to prevent it.
- Developing a heat illness prevention plan that includes strategies for preventing heat illness, such as providing access to shade, water, and air-conditioned areas.
- Encouraging employees to drink water frequently and to take frequent breaks in a cool area.
- Gradually increasing the workload and allowing more frequent breaks for new employees or those returning from a break.
- Providing employees with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for the job, such as hats and light-colored, loose-fitting clothing.
An informative resource to check out about heat illness guidelines across various states is the OSHA website. Additionally, you can visit your state's Department of Labor website for more information on state-specific regulations and guidelines for heat illness prevention in the workplace.
Talk To Your Boss
If you feel that the temperature in your warehouse is too hot or way too cold, it's important to raise your concerns with your boss or supervisor. Here are some tips for having a productive conversation about workplace temperatures:
- Gather evidence:
Before approaching your boss, try to gather as much evidence as possible about the temperatures in the warehouse. This may include taking temperature readings with a thermometer, documenting any discomfort or health issues you or your coworkers are experiencing, and noting equipment failures or other issues that may have been caused by extreme temperatures.
- Prepare:
Think about what you want to say to your boss and how you can present your concerns in a clear and concise manner. Consider potential solutions or recommendations you have for improving the temperature in the warehouse.
- Schedule a meeting:
Rather than raising your concerns in the middle of a busy workday, try to schedule a meeting with your boss during a time when you can have an undisturbed conversation. This will give you an opportunity to fully explain your concerns and discuss potential solutions.
- Be respectful and professional:
It's important to approach this conversation with respect and professionalism, even if you feel strongly about the issue. Avoid becoming confrontational or accusatory, and focus on finding a solution rather than placing blame.
- Follow up:
After the meeting, be sure to follow up with your boss to see if any action has taken place to address the problem. If there is no improvement, consider seeking the help of a higher-level manager or HR representative, if necessary.
By following these steps, you can have a productive conversation with your boss about the temperature in the warehouse and work together to find a solution. Remember to stay focused on the issue at hand and remain calm and respectful, even if you feel strongly about the matter.
Benefits of Investing in MacroAir Fans
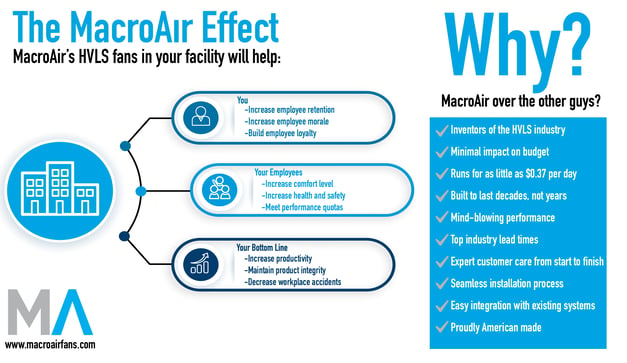
MacroAir's High Volume, Low Speed (HVLS) fans offer a number of benefits for warehouses and other large facilities. These fans range from 6-24 feet in diameter and are able to circulate the same amount of air as 34 smaller fans, thanks to the large column of air that can travel greater distances.
Large MacroAir ceiling fans provide comfort all year-round by circulating air in the summer to keep workers cool and running it in reverse in the winter to distribute warmer air. They are also much quieter than smaller fans, with noise levels ranging from 39-61 decibels, depending on the size and type of fan.
Additionally, MacroAir HVLS ceiling fans are energy-efficient and cost-effective. They can reduce energy costs by up to 30% and pay for themselves in as little as 6 months, depending on environmental factors. One large shop ceiling fan can affect up to 20,000 square feet of space. Proper installation is key to ensuring optimal performance and less noise.Many manufacturers offer professional installation for larger facilities.
Final Thoughts
It is important to follow OSHA's recommended temperature range of 68-76° F, as very high or very low temperatures can lead to health issues, mistakes, and damage to equipment and products. Although there aren’t set OSHA warehouse temperature regulations, it is highly recommended to maintain a certain temperature range in industrial spaces.
Employers should take steps to ensure their warehouse temperatures are comfortable for employees and address any temperature-related concerns promptly. Investing in solutions, such as MacroAir HVLS ceiling fans, can also help regulate temperatures and improve air quality in your warehouse. By following OSHA's recommendations and implementing effective temperature management strategies, warehouse managers can create a safer and more comfortable work environment for their employees.
If you would like to learn more about the benefits of MacroAir fans for warehouses, click the link below.

